 |
|
|
|
 |
|
|
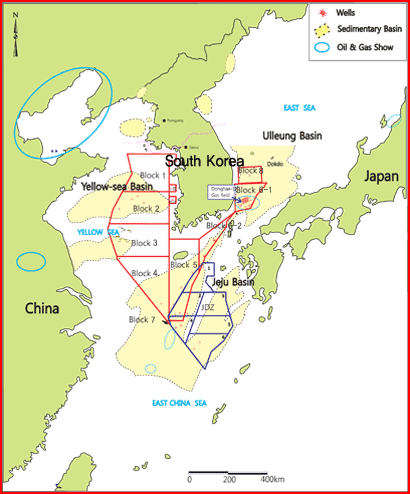
Korea is surrounded by the Yellow Sea, the East Sea, and the South Sea with extensive continental shelves of 300,000 ㎢ which have the potential for oil and gas exploration. Western oil companies such as Gulf, Shell, and Koam Corporation explored oil and gas in shallow waters in 1970s and 1780s. Since KNOC had been established in 1979, it began working on the shelves continuously and has acquired 116,549 L-㎞ of 2D seismic data and 7,519 ㎢ of 3D seismic data and has drilled 47 wells so far.
In 1998, KNOC discovered a commercially viable gas field in Block 6-1 in the East Sea. The field, which was named Donghae-1, is about 60 ㎞ away from Ulsan in the southern region of Korea. Donghae-1 gas field was on stream in 2004 and has produced gas and condensate so far. In 2014, KNOC initiated Donghae-2 gas project to develop a near field discovery with a single producer which was successfully subsea tie-backed to Donghae-1 platform in 2016.
Korean government has divided the offshore area into 12 blocks(excluding JDZ) and some blocks are currently authorized for licensees to explore. A list of blocks and their status are shown in following table.
|
| |
| Block |
Area |
Status |
| 1 |
34,470 |
KNOC |
| 1-2 |
414 |
Open |
| 1-3 |
422 |
Open |
| 2 |
39,446 |
KNOC |
| 2-2 |
423 |
Open |
| 3 |
41,620 |
KNOC |
| 4 |
43,195 |
KNOC |
| 5 |
44,529 |
KNOC |
| 6-1 |
12,917 |
6-1C : KNOC
6-1E : KNOC
6-1N : KNOC
6-1S : Open |
| 6-2 |
11,939 |
Open
Southern area is included in JDZ |
| 7 |
69,662 |
Most area is included in JDZ |
| 8 |
8,481 |
KNOC |
| JDZ |
82,557 |
Subzone 1,3,5,6 : Open
Subzone 2,4 : KNOC |
|
|
A large portion of the surrounding continental shelves consisting of Ulleung, Jeju and Yellow Sea basin has yet to be explored.
|
|
 |
Ulleung basin |
|
|
Located in the East Sea between Korea and Japan, the Ulleung Basin has 10 kilometer thick clastic sediments in its southwestern margin where the Donghae-1 gas field was discovered. The basin consists of two exploration blocks, 6-1 in the south and 8 in the north, which are 12,917 ㎢ and 8,481 ㎢, respectively.
Block 6-1 was first explored by Royal Dutch Shell Oil in 1971. The company drilled a first exploratory well in offshore of Korea, although not tested, encountered a number of gas shows. KNOC has paid attention to Block 6-1 after 1983. Since then, it has conducted numerous seismic surveys and 24 wells drilling campaigns. These efforts resulted in thirteen minor discoveries of gas and two major discoveries of economically producible gas reserves in 1998, 2005 as described above(see Donghae-1, Donghae-2 section below for further information).
Currently, there are 2 active licenses in the Ulleung basin.
|
| |
| Name |
License |
Area(㎢) |
Stake |
Operator |
| 8/6-1N |
Concession |
12,560 |
KNOC |
100% |
KNOC |
| 6-1C&E |
Concession |
4,002 |
KNOC |
100% |
KNOC |
|
|
KNOC and Woodside Energy Limited which hold a 50% working interest, respectively signed the concession contract with Korea’s Ministry of Trade, Industry & Energy(MOTIE) to explore deepwater blocks, Block 6-1 North and Block 8, in 2007. During 10 years contracting period, two exploration wells, Jujak-1 and Hongge-1 were drilled in 2012 and 2015, respectively and confirmed the presence of gas in deepwater region. KNOC and Woodside started to explore same area again in 2019 with a new concession contract and acquired new 3D seismic data during the 1st exploration period. Woodside decided not to enter the 2nd exploration period and KNOC took over their working interest and operatorship. Now KNOC is soley operating the project in the 2nd exploration period.
KNOC has entered new concession agreement with MOTIE in Block 6-1 C&E early 2020 and is focusing on deep water potential in the area. KNOC drilled a well and a post well evaluation is under way. Also another seismic data acquisition is just finished followed by interpretation work to define other drillable prospects in the adjacent deepwater area.
|
| |
 |
Jeju Basin |
|
|
The Jeju Basin where Block 4, 5, 6-2 and 7 are set is a tertiary basin located among Korea, Japan, and China. The young sedimentary area is defined by a series of NE-SW trending half-grabens with the highs separating the Socotra subbasin from the Domi subbasin. The Socotra subbasin spans the southern part of Block 4 and the Domi basin lies in Block 6-2. The southern boundary of the Jeju Basin meets the northern boundary of the Joint Development Zone (JDZ) between Korea and Japan.
Western oil companies, including Gulf, Texaco, and Shell began exploration in blocks 4, 5, and 6-2 in early 1970s. They obtained 12,781 L-㎞ of 2D seismic data and drilled one exploratory well in Block 4. In Block 5, 2D data of 11,995 L-㎞ was acquired and four wells were drilled, and in Block 6-2, 2D data of 12,786 L-㎞ was gathered and three wells were drilled. Through these activities, they discovered several oil and gas shows.
JDZ(Joint Development Zone) was set in 1978 based on the agreement between Korean and Japanese governments for 50 years period. The JDZ has been less explored compared to other blocks due to the nature of the joint development, that allows only Korea-Japan joint activities in the area. So far 19,571 L-㎞ of 2D seismic data and 563 ㎢ of 3D seismic data obtained in the area and seven exploratory wells drilled. Three of them resulted in oil and gas shows.
Early 2020, KNOC has acquired exploartional licences for 2 subzones from Korean government and been waiting for Japanese licensee to be designated for further exploration.
|
| |
Jeju Basin
| Name |
License |
Area(㎢) |
Licensee |
Operator |
| Korea |
Japan |
JDZ
(Subzone2,4) |
Concession |
12,560 |
KNOC |
- |
- |
|
|
Early 2022, KNOC has also acquired exploartional licences for block 4, block 5 and run 3D seismic campaign to evaluate hydrocarbon potential across Jeju basin including JDZ.
|
| |
| Name |
License |
Area(㎢) |
Stake |
Operator |
| 4 |
Concession |
43,195 |
KNOC |
100% |
KNOC |
| 5 |
Concession |
44,529 |
KNOC |
100% |
KNOC |
|
| |
 |
Yellow Sea Basin |
|
|
The Yellow Sea Basin is composed of Gunsan and Heuksan basin which are dissected by basement highs and has mainly three exploration blocks, 1, 2, and 3 with three satellite blocks, 1-2, 1-3, 2-2. The exploration activities include 35,827 L-km of 2D seismic data, 298 ㎢ of 3D seismic data and 6 exploration wells mostly carried by Texaco, Gulf, Marathon and KNOC before 2000s.
Late 2023, KNOC acquired exploration licences for Block 1, Block 2 and Block 3 as a part of extensive exploration campaign in Korean continental shelf.
|
| |
| Name |
License |
Area(㎢) |
Stake |
Operator |
| 1 |
Concession |
34,470 |
KNOC |
100% |
KNOC |
| 2 |
Concession |
39,446 |
KNOC |
100% |
KNOC |
| 3 |
Concession |
41,620 |
KNOC |
100% |
KNOC |
|
|
Department Contacts Updated
| Updated : 2026-02-19 |
Department : E&P-Domestic Business Development Dept. |
Contacts : +82)52-216-3108 |
|